North Korean hackers are using fake job offers and disguised app updates to sneak malware onto Macs, and while Apple’s latest XProtect update blocks some threats, others are still slipping through.
Security researchers from SentinelLabs have identified fresh variants of a North Korean malware family, dubbed “FlexibleFerret,” which is actively exploiting macOS users. The malware is part of a broader campaign known as “Contagious Interview,” where attackers pose as recruiters to trick job seekers into installing malicious software.
Apple responded with an XProtect signature update to counter these threats, blocking several variants, including FROSTYFERRET_UI, FRIENDLYFERRET_SECD, and MULTI_FROSTYFERRET_CMDCODES.
XProtect is Apple’s built-in malware detection and removal tool for macOS, designed to identify and block known malicious software. It runs silently in the background, using regularly updated security signatures to detect threats when files are downloaded or executed.
Unlike traditional antivirus software, XProtect operates at the system level with minimal user interaction, automatically protecting Macs without requiring manual scans.
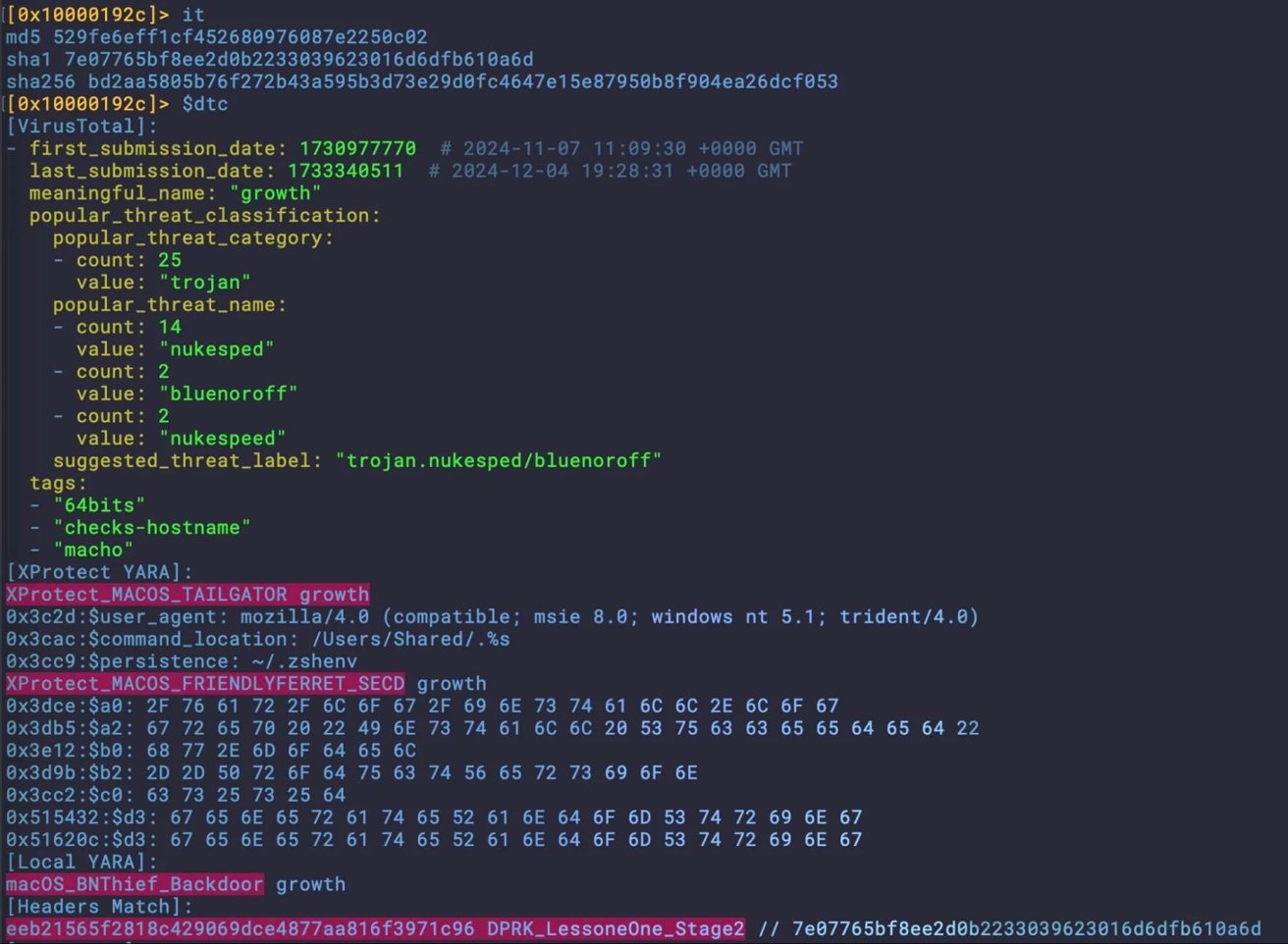 Some malware components found in FlexibleFerret share similarities with the Stage 2 payloads used in North Korea’s Hidden Risk campaign. Image credit: SentinelOne
Some malware components found in FlexibleFerret share similarities with the Stage 2 payloads used in North Korea’s Hidden Risk campaign. Image credit: SentinelOne
The malware campaign has evolved from earlier DPRK-attributed threats discovered in December and January. Attackers are using deceptive tactics such as fake Chrome updates and disguised Zoom installers to infect macOS systems.
The malware’s persistence mechanisms and data exfiltration methods indicate a well-funded, state-backed operation.
How the malware spreads
The FlexibleFerret malware primarily spreads through social engineering. Victims are tricked into downloading a seemingly legitimate app, such as VCam or CameraAccess, after encountering an error message during a fake job interview.
In reality, these apps install a malicious persistence agent that runs in the background, stealing sensitive data. One identified package, versus.pkg, contains multiple malicious components, including InstallerAlert.app, versus.app, and a rogue binary named zoom.
Once executed, the malware installs a launch agent to maintain persistence and communicates with a command-and-control server via Dropbox.
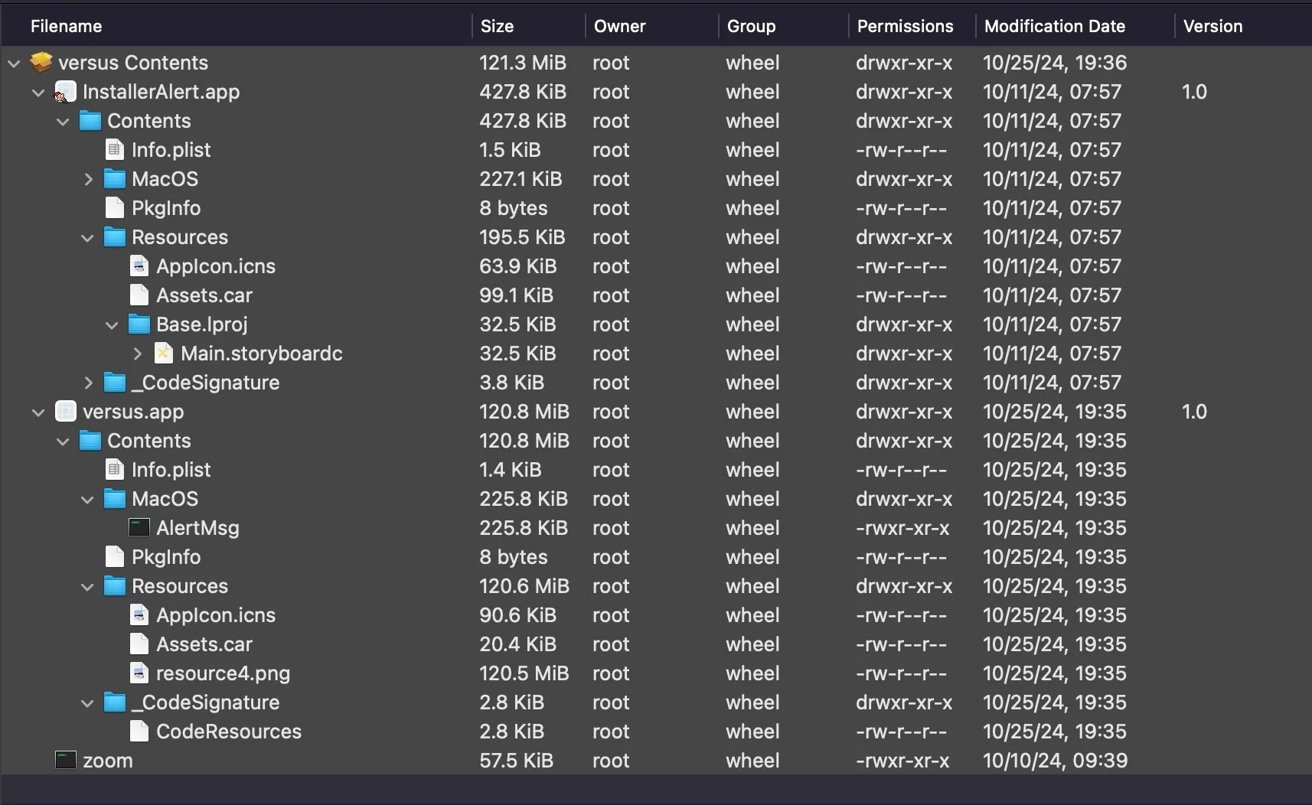 File contents of the FlexibleFerret dropper, versus.pkg. Image credit: SentinelOne
File contents of the FlexibleFerret dropper, versus.pkg. Image credit: SentinelOne
Apple’s latest XProtect update blocks key malware components disguised as macOS system files, including com.apple.secd. However, some FlexibleFerret variants remain undetected, highlighting the evolving nature of these threats.
Protecting your Mac
Mac users should be cautious when downloading software from untrusted sources and skeptical of unexpected software installation prompts. Apple’s built-in security measures provide a first line of defense, but additional endpoint security solutions can help detect and block emerging threats.
Tools like Malwarebytes, Sophos Home, and CleanMyMac X offer extra layers of protection against cyber attacks.